Innovative AI Use Cases for Enhancing Financial Inclusion in Low Income Countries
Introduction
Financial inclusion remains a significant challenge in Low Income countries, where large segments of the population lack access to basic banking and financial services. Innovative applications of Artificial Intelligence (AI) offer promising solutions to bridge this gap, making financial services more accessible, user-friendly, and efficient. This article explores several AI-driven use cases that can revolutionize financial inclusion in these regions, supported by relevant graphs to illustrate their impact and examples from Low Income countries.
AI-Powered Mobile Banking
Use Case: Mobile-Based Financial Services
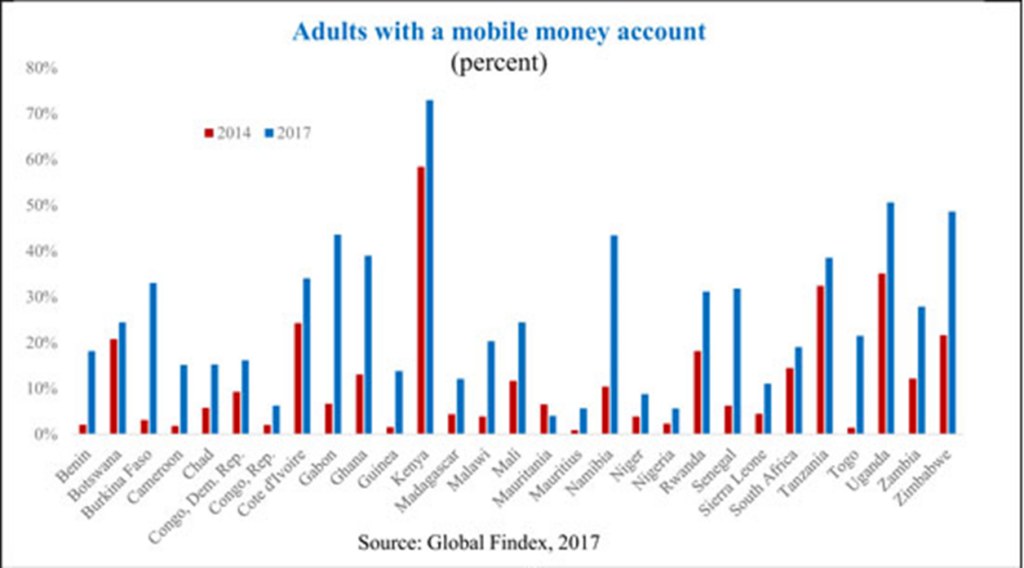
Mobile banking applications powered by AI can offer personalized financial services to users in remote areas. These apps can include features like voice-activated interfaces, chatbots for customer support, and personalized financial advice. As shown in Figure 1, the number of mobile money accounts increased significantly between 2014 and 2017.
Figure 1: Growth of Mobile Money Account in Low Income Countries
Example: M-Pesa in Kenya
M-Pesa, a mobile-based money transfer and microfinancing service, has revolutionized financial inclusion in Kenya. By using AI to manage transactions and provide customer support, M-Pesa has enabled millions of Kenyans to access banking services without needing a traditional bank account. As shown in Figure 1, the number of mobile money accounts increased to more than 70% in 2017.
Benefits:
- Accessibility: Provides banking services to users without access to physical banks. Mobile money accounts increased to 70% in Kenya at 2017 (figure 1).
- Personalization: Tailors services to individual needs, enhancing user experience.
- Efficiency: Reduces operational costs and improves service delivery.
AI-Driven Credit Scoring
Use Case: Alternative Data for Credit Scoring
Traditional credit scoring systems often exclude individuals without formal credit histories. AI can analyze alternative data sources such as mobile phone usage, social media activity, and transaction history to assess creditworthiness.
Example: Branch in Africa
Branch, a fintech company operating in several African countries, uses AI to assess creditworthiness by analyzing mobile phone data. This approach has enabled many people who lack traditional credit histories to access loans.
Benefits:
- Inclusion: Extends credit to underserved populations.
- Accuracy: Provides a more comprehensive assessment of credit risk.
- Growth: Encourages financial institutions to expand their customer base.
Automated Financial Education
Use Case: AI-Powered Educational Platforms
AI can deliver personalized financial education through mobile apps, helping users understand financial products, manage budgets, and make informed financial decisions.
Example: Ruangguru in Indonesia
Ruangguru is an Indonesian edtech company that uses AI to provide personalized learning experiences. Its financial literacy programs are helping young Indonesians understand money management and financial planning.
Benefits:
- Empowerment: Equips users with knowledge to make better financial decisions.
- Engagement: Uses interactive tools and personalized content to keep users engaged.
- Scalability: Reaches a large audience with minimal resources.
Fraud Detection and Prevention
Use Case: AI for Fraud Monitoring
AI algorithms can detect fraudulent activities in real-time by analyzing transaction patterns and identifying anomalies. As shown in Figure 2, the top AI use cases for cybersecurity include network security, data security, and more.
Figure 2: Top AI Use cases for cybersecurity
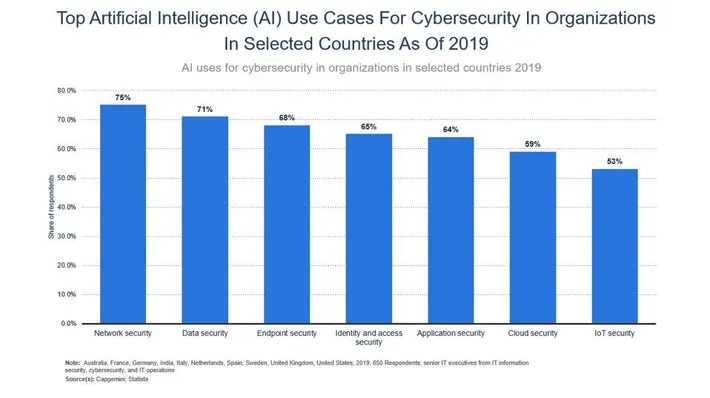
Source: Forbes
Example: Paystack in Nigeria
Paystack, a Nigerian payment processing company, uses AI to detect and prevent fraud. By analyzing transaction data in real-time, Paystack can identify suspicious activities and protect users from financial fraud.
Benefits:
- Security: Protects users and financial institutions from fraud.
- Trust: Builds trust in digital financial services.
- Efficiency: Reduces the need for manual fraud investigation.
Microfinance and Peer-to-Peer Lending
Use Case: AI in Microfinance Platforms
AI can enhance microfinance and peer-to-peer lending platforms by matching borrowers with suitable lenders and predicting repayment behaviors. As shown in Figure 3, if we assume a minimum annual growth rate of 11% for global microfinance, the market size of global microfinance in 2032 will double compared to 2024.
Figure 3: Growth in Global Microfinance Market Size
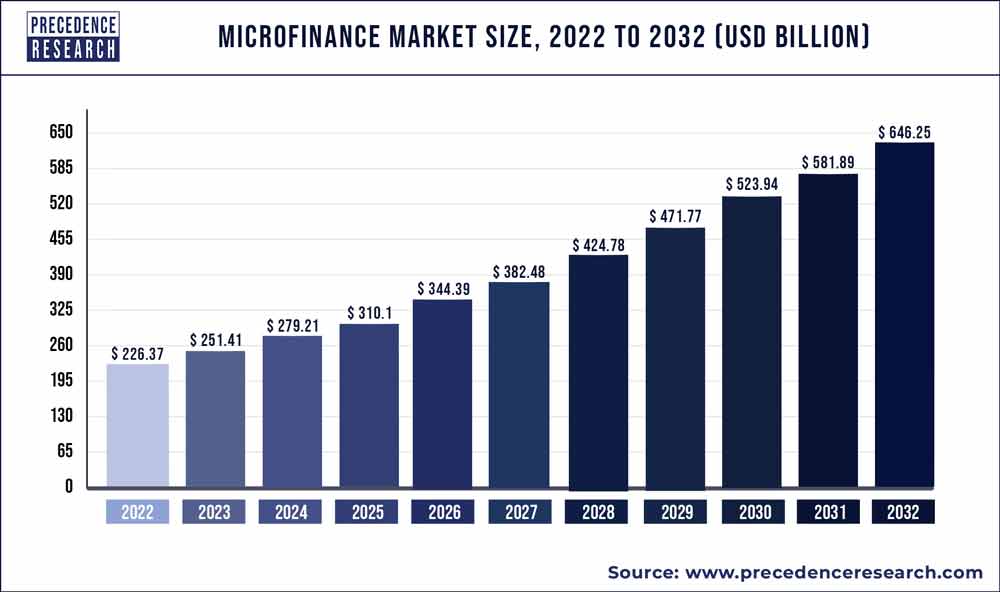
Example: Tala in the Philippines
Tala, a fintech company operating in the Philippines, uses AI to offer microloans to individuals without access to traditional banking services. By analyzing mobile phone data, Tala assesses creditworthiness and provides instant loans to its users.
Benefits:
- Accessibility: Provides funding opportunities for small businesses and entrepreneurs.
- Efficiency: Streamlines the lending process.
- Inclusivity: Expands financial services to underserved communities.
Conclusion
AI offers transformative potential for enhancing financial inclusion in Low Income countries. By leveraging AI-driven solutions such as mobile banking, alternative credit scoring, automated financial education, fraud detection, and microfinance platforms, financial services can become more accessible, user-friendly, and efficient. These innovations not only address the immediate needs of underserved populations but also pave the way for sustainable economic growth.
References
- Deloitte Insights: Top 10 Business Insights
- World Bank Data: Mobile Banking Statistics
- Financial Inclusion Reports by International Monetary Fund (IMF)
